Every square foot of a grocery store has the potential to increase sales, influence customer behavior, and improve the overall shopping experience—if designed strategically. A well-structured grocery store layout does more than just organize products; it guides shoppers’ movements, encourages impulse purchases, and maximizes high-margin sales.
For grocery retailers and supermarket chains, an optimized store layout can mean the difference between a profitable, high-traffic store and one that struggles with slow-moving inventory and lost sales opportunities. Smart placement of key departments, staple goods, and promotional displays can keep customers shopping longer, spending more, and returning frequently.
This guide explores proven grocery store layout strategies, the psychology behind effective merchandising, and actionable tactics to create a more profitable and customer-friendly store. Whether you’re designing a new store or optimizing an existing one, these insights will help you make every aisle count.
What Is the Best Layout for a Grocery Store?
Choosing the best grocery store layout plan is crucial for optimizing customer flow, maximizing product exposure, and increasing sales. A well-structured grocery store floor plan should create a smooth shopping experience while strategically guiding customers through key sections to encourage higher spending.
While the ideal store layout design depends on store size, target audience, and product offerings, some of the most effective grocery store layouts include:
The grid layout is the most commonly used grocery store layout, featuring long, straight aisles that organize products into sections (e.g., dairy, bakery, and household essentials). It is efficient, easy to navigate, and maximizes product exposure.
Best for: Large grocery stores, supermarkets, and retail chains.
Key Benefits:
- Maximizes shelf space for a wide product assortment.
- Guides shoppers past multiple categories, increasing impulse buys.
- Creates a predictable and organized shopping experience.
Challenges: Can feel rigid, limiting spontaneous product discovery.
Tip: Place staple items like milk and bread at the back to encourage shoppers to walk through more aisles.
For stores with limited space, the herringbone layout features angled aisles, maximizing product display while allowing for customer flow. This is common in small grocery stores, specialty markets, and convenience stores.
Best for: Compact stores that need high product density.
Key Benefits:
- Uses angled shelving to make the most of limited space.
- Side walls and endcaps are great for promotions.
- Encourages customers to explore multiple sections.
Challenges: Narrow aisles can cause congestion, and limited visibility may increase theft risks.
Tip: Install security cameras and mirrors to improve visibility and reduce shrinkage.
The loop layout, or racetrack layout, features a single main aisle that guides customers through every major section before reaching checkout. This design ensures maximum product exposure and works well for retailers looking to increase impulse purchases.
Best for: Large supermarkets, department-style grocery stores, and specialty markets.
Key Benefits:
- Directs customers through key departments like fresh produce, bakery, and deli.
- Encourages browsing and engagement with creative displays.
- Works well for seasonal or promotional sections.
Challenges: Can be frustrating for shoppers in a hurry if shortcuts aren’t available.
Tip: Include shortcut aisles for customers who need only a few essentials.
Beyond the grid, herringbone, and loop layouts, other grocery store layout designs can enhance customer experience and increase sales. Choosing the best grocery store layout plan depends on factors like store size, customer behavior, and product variety. Here are additional effective store layout designs for grocery retailers:
The free-flow layout removes the rigid structure of aisles, allowing customers to browse more naturally and interactively. Unlike traditional grocery store floor plans, this design is less structured and works well for stores that focus on experience-driven shopping.
Best for: Specialty grocery stores, organic markets, and boutique food retailers.
Key Benefits:
- Encourages browsing, increasing time spent in-store.
- Creates a premium shopping experience with open spaces and inviting displays.
- Allows for flexible product placement and seasonal merchandising.
Challenges: Can feel disorganized if not well-executed, leading to confusion in navigation.
Tip: Use clear signage and logical product groupings to maintain a smooth flow while still offering a relaxed shopping experience.
The spine layout features a central main aisle (spine) with smaller aisles branching off, leading customers through different sections of the store. This hybrid grocery store layout blends the efficiency of a grid layout with the exploratory nature of a free-flow plan.
Best for: Medium-sized grocery stores and specialty food retailers.
Key Benefits:
- Guides customer movement without feeling too rigid.
- Maximizes product exposure while keeping a natural flow.
- Works well for stores with a mix of staple and specialty products.
Challenges: Requires careful product placement and signage to prevent shoppers from missing key sections.
Tip: Position high-margin and seasonal products along the spine to increase visibility and encourage impulse buys.
By integrating the right store layout design, grocery retailers can create a more efficient and profitable shopping experience. Each grocery store floor plan has unique advantages, so selecting the best grocery store layout plan depends on store size, product assortment, and customer preferences.
Store layout example created in PlanoHero planogram software
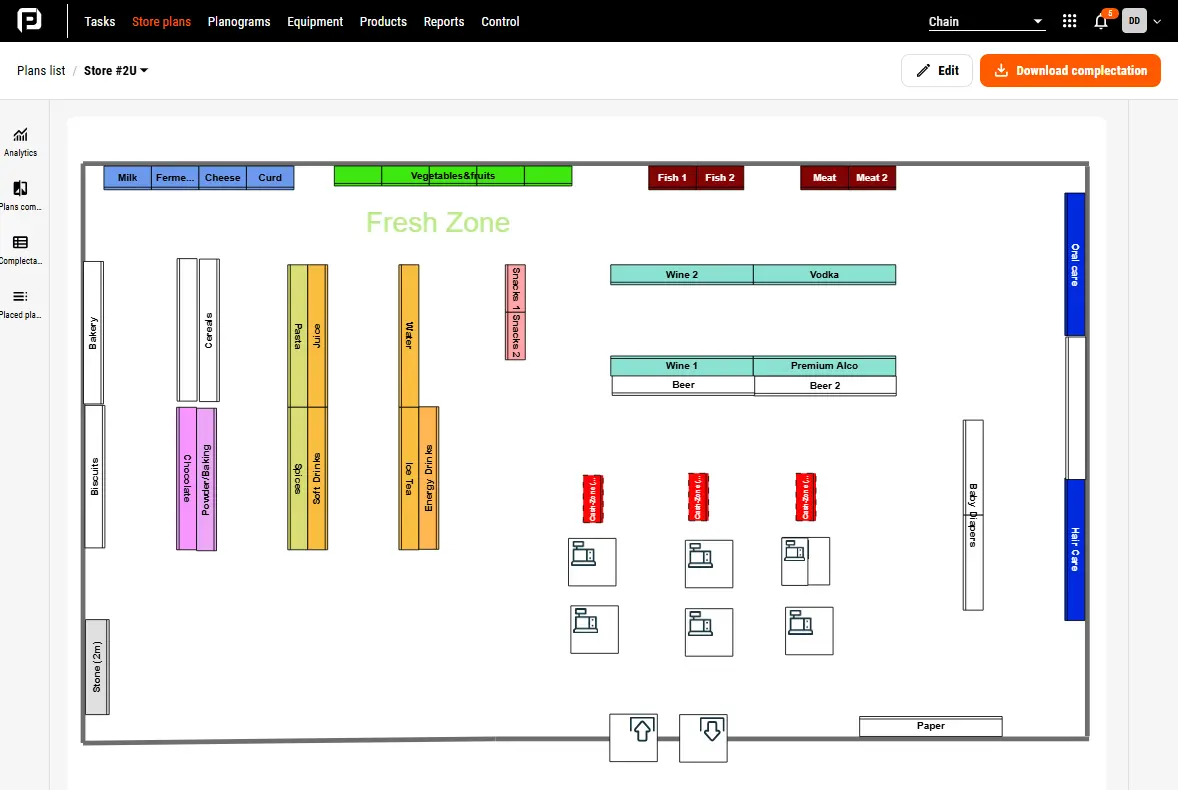
This grocery store follows a Grid Layout with elements of a Loop (Racetrack) Layout.
Elements of a Grid Layout:
The store features long, straight aisles that organize products into clear sections (e.g., Bakery, Dairy, Beverages, Snacks, Alcohol). Essential categories like vegetables & fruits, dairy, and meat are positioned at strategic points to encourage movement across multiple aisles.
Elements of a Loop (Racetrack) Layout:
- The Fresh Zone (fruits, vegetables, meat, and fish) is placed at the top of the store, guiding customers through an intentional shopping path.
- Checkout counters are centrally positioned near the store entrance/exit, ensuring customers pass impulse-buy areas before leaving.
- High-margin products like alcohol and snacks are placed along major walkways, increasing exposure.
Essential Tips for an Effective Grocery Store Layout Strategy
A well-structured grocery store layout strategy not only enhances the shopping experience but also drives sales and customer engagement. By strategically placing high-demand products, creating intuitive traffic flow, and using smart merchandising techniques, retailers can optimize their grocery store floor plan for maximum profitability. Below are key strategies to consider when designing the best grocery store layout plans.
First impressions matter, and placing a vibrant, well-stocked produce section at the front of the store sets the tone for a fresh, high-quality shopping experience.
Why it works:
- Bright colors and fresh scents put customers in a positive shopping mindset, increasing engagement.
- Encourages impulse purchases as shoppers associate fresh produce with health and quality.
- A spacious layout allows multiple shoppers to browse comfortably without congestion.
Tip: Enhance the experience with seasonal produce displays and eye-catching signage to highlight promotions.
Staple products like milk, bread, and eggs should be placed at the back of the store to increase overall store traffic.
Why it works:
- Forces customers to walk past multiple aisles, increasing product exposure.
- Encourages unplanned purchases along the way, boosting cross-selling opportunities.
- Helps distribute foot traffic evenly, preventing bottlenecks at the entrance.
Tip: Place high-margin or impulse-buy items along the path to staple goods to increase additional sales.
The smell of freshly baked bread and pastries is a powerful trigger that influences purchasing behavior.
Why it works:
- Activates appetite and cravings, encouraging impulse buys.
- Creates a warm, welcoming atmosphere, reinforcing brand quality.
- Sets your store apart as a full-service grocery destination.
Tip: Feature pre-packaged bakery items near the checkout to capture last-minute purchases.
With the rise of meal kit services, grocery stores can capitalize on convenience by placing related meal ingredients together.
Why it works:
- Simplifies shopping by making meal planning easier.
- Encourages customers to buy a full set of ingredients instead of just one.
- Boosts basket size with pre-made meal solutions.
Example: Display pre-made pizza dough, marinara sauce, cheese, and toppings together for an easy dinner solution.
Customers are more likely to buy complementary products when they are conveniently placed together.
Why it works:
- Makes shopping more intuitive and efficient.
- Increases impulse purchases by jogging customers’ memory.
- Reduces the chance of customers forgetting an essential item.
Example: Place chips and salsa near beer and soda or pasta next to sauces and Parmesan cheese.
A well-designed checkout area improves customer satisfaction and reduces cart abandonment.
Why it works:
- Minimizes long wait times, preventing frustration.
- Encourages last-minute impulse buys with well-placed small items.
- Keeps traffic flowing smoothly for a better shopping experience.
Tip: Invest in self-checkout kiosks to speed up transactions for customers with small baskets.
Busy shoppers appreciate quick, convenient options, making grab-and-go items a high-margin category.
Why it works:
- Appeals to customers in a hurry, leading to quick purchases.
- Increases sales without adding extra shopping time.
- Works especially well for coffee, pre-made sandwiches, and snack items.
Tip: Keep high-turnover grab-and-go products near checkout lanes and store entrances to capture impulse purchases.
Strategic product placement can direct customer attention to best-selling or promotional items.
Why it works:
- Endcaps (aisle ends) ensure top-selling products are visible from multiple angles.
- Placing high-margin items at eye level increases the likelihood of purchase.
- Child-targeted products at lower shelves increase "pester power" purchases from parents.
Tip: Rotate seasonal and promotional products at high-visibility locations to keep the store fresh and engaging.
The Psychology Behind Grocery Store Layout Strategy
Grocery stores use subtle psychological tactics to encourage spending and improve the shopping experience. Here’s how:
- Music & Scents – Slow, calming music encourages longer shopping times, while pleasant smells (like fresh bread or coffee) trigger hunger and impulse buys.
- Spacious Entrances – Wide, open entrances create a welcoming atmosphere, while cluttered entryways can discourage shoppers from staying.
- Impulse Zones at Checkout – Small, affordable items like snacks, gum, and magazines tempt shoppers while they wait, boosting last-minute sales.
- No Windows, No Clocks – Limited access to natural light or time cues keeps shoppers inside longer, increasing overall spending.
By applying these psychological principles, grocery retailers can design a more engaging and profitable store layout strategy.
Final Thoughts on Grocery Store Layout Strategy
By applying these grocery store layout strategies, retailers can create an efficient and profitable shopping environment. Whether optimizing a small convenience store or a large supermarket, a well-planned grocery store floor plan plays a crucial role in customer flow, product visibility, and overall sales performance.
A carefully designed store layout strategy ensures that every aisle, display, and shelf works toward increasing revenue and improving the customer experience.
Looking for a service to create planograms?
Try a free demo version of PlanoHero