The retail shelf is now a key area of strategic competition. Every product competes for visibility, attention, and space — both in physical aisles and digital storefronts. A brand’s success depends not only on product quality but also on how effectively it occupies and manages its shelf strategy.
What Is a Retail Shelf Strategy?
A retail shelf strategy defines where, how, and why products are placed within a store or online catalog. It involves decisions about product assortment, shelf placement, facings, price hierarchy, and adjacency — all of which influence a shopper’s path to purchase.
At its core, a shelf strategy is about visibility and persuasion. The average shopper spends just a few seconds glancing at a category before deciding what to pick up. That means your product’s location, design, and message must all align to attract attention and drive conversion.
An effective shelf strategy is never random — it’s engineered. Each shelf placement is informed by sales data, shopper insights, and category management principles. Well-planned shelf positioning ensures that every product receives optimal visibility and contributes to overall category growth.
Why Shelf Placement Matters in Retail
Shelf placement directly impacts sales performance. According to merchandising research, products placed at eye level can generate up to 23% higher sales than those located on lower shelves. The reason is simple: visibility drives attention, and attention drives conversion.
In addition, endcaps and promotional displays — high-traffic areas at the end of aisles — often lead to impulse purchases, making them premium display zones. Products placed in these areas are more likely to be noticed by both loyal customers and casual browsers.
Effective shelf placement also reinforces brand identity. Grouping similar SKUs together creates visual consistency and helps consumers quickly recognize and navigate a brand’s portfolio. Known as brand blocking, this technique uses color and packaging alignment to turn a section of shelving into a cohesive brand experience.
The Psychology Behind Shelf Strategies
Winning at the shelf requires understanding human behavior. Shoppers make thousands of unconscious decisions during a store visit, and retail shelf strategies play a critical role in shaping those decisions.
Eye-level zones capture immediate attention and should house top-performing or high-margin products. Lower shelves are often used for bulk items or children’s products, as they match their line of sight. Upper shelves may host premium or specialty items aimed at specific target segments.
The visual flow of the shelf — from left to right or top to bottom — also affects buying behavior. Shoppers typically scan shelves following familiar reading patterns. Placing hero products on the natural focal points of this flow can improve recognition and sales.
Even color psychology influences perception. Bright, high-contrast packaging attracts impulse buyers, while minimalist designs appeal to shoppers seeking premium quality.
Shelf Space Optimization in Retail Stores
Every centimeter of retail shelf space in a store carries measurable financial value. Retailers and manufacturers negotiate not only for how much space a product receives but also for where it appears.
To optimize space effectively, brands must use data-driven insights to justify their shelf strategy decisions. This involves analyzing:
- Sales velocity by SKU and location
- Shopper traffic patterns and dwell time
- Competitor adjacency and category trends
- Product profitability and price elasticity
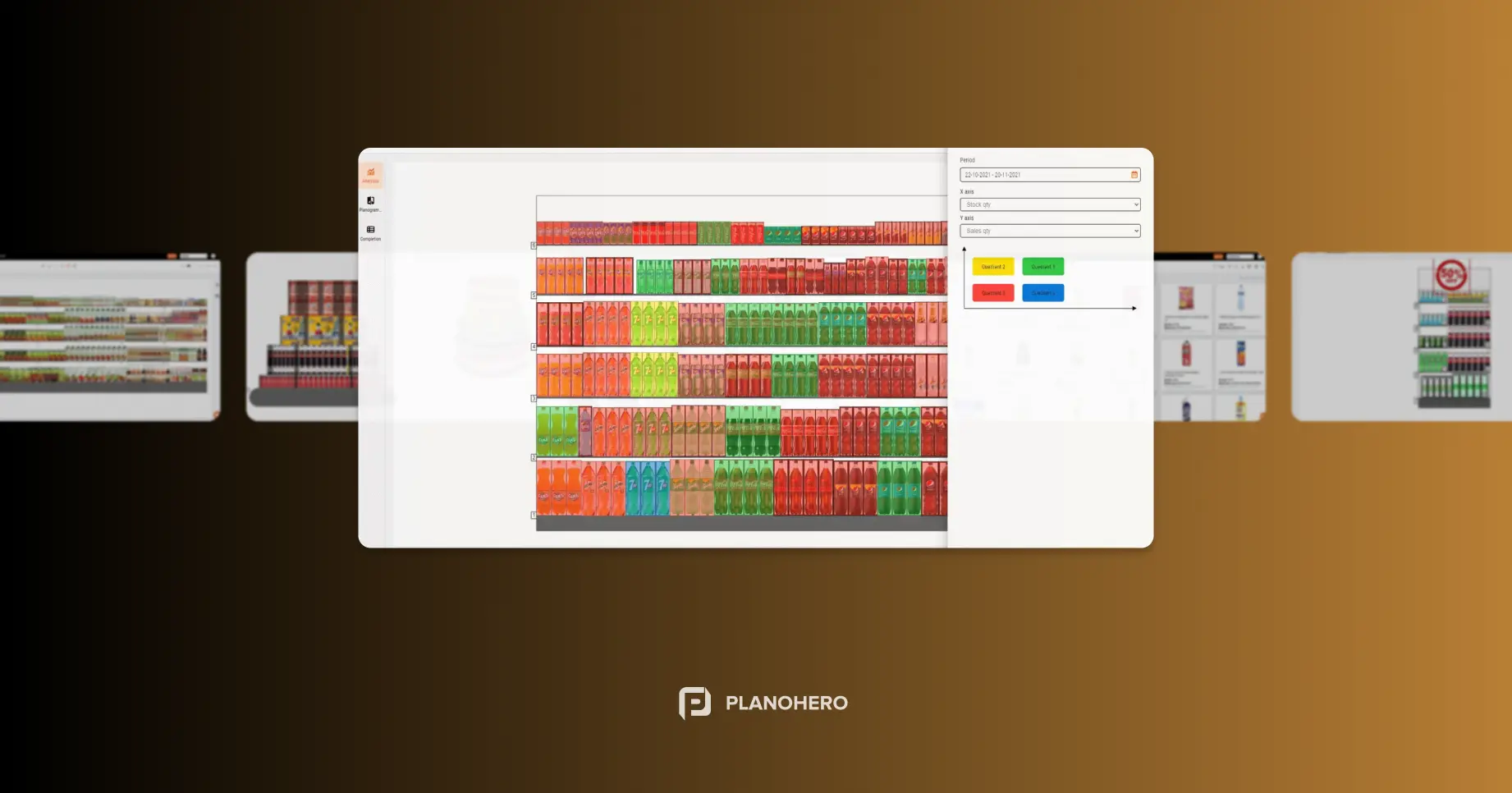
Modern merchandising teams use planogram software to visualize these decisions before products reach the shelves. 3D planogram simulations allow category managers to test multiple layouts, compare facings, and predict which configurations deliver the best ROI.
When executed correctly, shelf strategies create a seamless shopping experience where products appear exactly where shoppers expect them — and where they are most likely to buy.
The Role of Pricing and Product Architecture
Pricing is a critical extension of retail shelf strategy. Consumers subconsciously associate price positioning with value and quality.
There are three main pricing frameworks that influence shelf performance:
- High–Low Pricing: Products are introduced at a higher price, followed by timed discounts to stimulate urgency.
- Everyday Value Pricing: A consistent, competitive price that builds long-term trust and loyalty.
- Price/Pack Architecture: Offering different sizes or packaging formats at tiered price points allows brands to occupy more shelf area and appeal to various budgets.
Combining pricing strategy with effective shelf planning ensures that products not only attract attention but also convert browsers into buyers.
Planograms and Category Management
Planograms are at the heart of any retail shelf strategy. A planogram is a visual or digital model that defines how and where products should be placed on shelves.
Strong planogram execution ensures:
- Consistent brand presentation across stores
- Efficient use of available space
- Balanced category representation and customer satisfaction
When brands manage their planograms proactively, they maintain greater control over how their products appear and perform across stores.
Platforms such as PlanoHero help brands and category managers plan, execute, and monitor planograms with precision. The system automates shelf layout creation, generates product libraries, and provides analytical reports. PlanoHero improves workflow efficiency and ensures visual compliance across multiple retail locations.
Measuring Shelf Strategy Effectiveness
The most effective retail shelf strategy is continuously refined using accurate performance data. Brands should track a mix of quantitative and qualitative KPIs to understand what drives conversion, including:
- Sales per linear foot – revenue generated by each shelf segment
- Planogram compliance rate – percentage of stores following approved layouts
- Out-of-stock frequency – how often products are unavailable
- Eye-tracking and shopper heatmaps – data that shows how consumers interact with displays
By comparing data across multiple retailers and store types, brands can identify which shelf combinations deliver the highest return and adjust accordingly.
Shelf Strategy Challenges
Even experienced brands face challenges when executing shelf initiatives. Common obstacles include:
- Retailer priorities: Retailers may favor private labels or established players. Brands should use sales data to justify premium space.
- Execution inconsistency: Poor in-store compliance leads to lost sales. Regular audits and digital verification improve accuracy.
- Competitive saturation: Overcrowded categories reduce visibility. Focus on packaging clarity and consistent presentation.
- Inventory management: Stock levels must align with demand to prevent empty shelves and missed opportunities.
Technology-Driven Shelf Strategy Enhancement
Modern shelf strategies are increasingly supported by technology. Artificial intelligence (AI) tools can analyze shelf images, detect planogram compliance, and identify out-of-stock situations.
PlanoHero helps category managers automate planogram creation, manage product data, and generate detailed visual layouts for retail chains. It simplifies collaboration across departments, improves planogram accuracy, and ensures consistency in retail execution.
A strong retail shelf strategy defines how products perform, how shoppers engage, and how brands grow within the store environment. By aligning placement with pricing logic, shopper behavior, and category management, brands can transform in-store visibility into measurable sales results. Those who manage shelf strategy with precision will achieve stronger brand consistency, higher shopper satisfaction, and improved profitability.
Winning in retail depends on understanding how to optimize each shelf space in retail store environments through structured data, design accuracy, and disciplined execution.
Looking for a service to create planograms?
Try a free demo version of PlanoHero